Table Of Content

Although more research is needed, it’s possible that treating this deficiency could help with hair regrowth. Female pattern baldness is largely genetic, affecting hair along the top of a woman’s head. Dramatic changes in the body can cause temporary hair loss. Giving birth, rapid weight loss, surgery and certain illnesses may cause more hair loss than usual, typically in the resting phase.

Free Healthbeat Signup
Furthermore, researchers have linked insufficient selenium, zinc, vitamin B12, riboflavin, and vitamin D to alopecia. Though hair loss can’t always be reversed, knowing what’s at the root of hair loss is critical in managing it. This article discusses factors that lead to thinning hair or bald spots, who’s at risk, and how to treat it. Losing your hair — whether the hair loss is temporary or permanent — can be emotionally difficult for many people. Most healthy people lose up to 100 strands of hair per day. As part of your hair’s growth cycle, new strands grow and take the place of the ones you shed.
How Is Female Hair Loss Treated?
Below are some frequently asked questions about hair loss. A doctor may recommend dietary changes and supplements to treat a nutritional deficiency. Treatment for this condition depends on the cause but may include a topical solution of minoxidil (Rogaine). AARP is a nonprofit, nonpartisan organization that empowers people to choose how they live as they age.
Cancer: Managing Symptoms Discussions
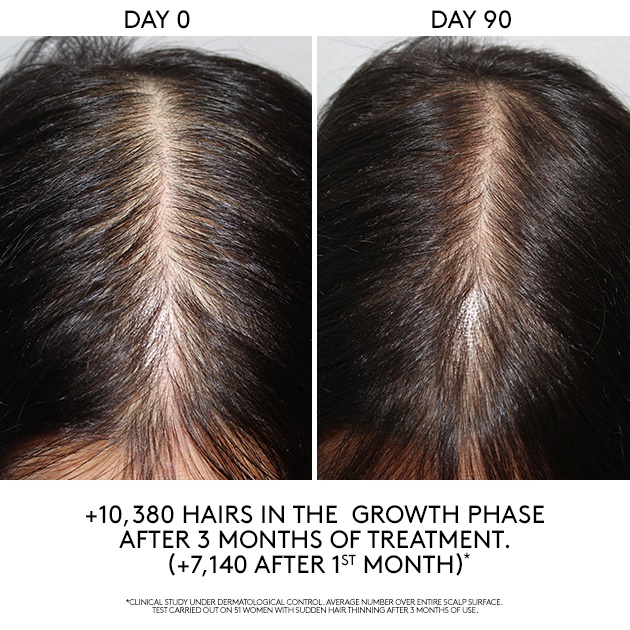
The caffeine also boosted hair root width and prolonged the growth phase of hair. It had a growth-promoting effect when tested on female hair follicles as well. Permanent hair loss results from progressive damage to your hair follicles, which are the structures in your skin that house and grow your individual strands of hair. “If you feel like you’re losing an excessive amount of hair, talk to your doctor. More than half of all women experience noticeable hair loss over time.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
Telogen effluvium is common, seen more frequently in women, and usually happens two to three months after a triggering event. It typically doesn't last more than six months, but if it does, it's considered chronic. Having excessive hair fall out, or shed, can be upsetting and stressful. However, it is common, and in most cases, it is also temporary. Some people may choose to use a scalp concealer, hair topper, or other product to cover hair loss.
The Hair Loss Guide for Women, Plus Regrowth Tips & Treatments - Allure
The Hair Loss Guide for Women, Plus Regrowth Tips & Treatments.
Posted: Thu, 22 Aug 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Other oft-used drugs include finasteride (Propecia) and spironolactone. By contrast, scarring alopecia, another autoimmune disease that causes hair loss, is often accompanied by itchiness, tenderness and scaling of the scalp. Scarring alopecia is the most devastating type of hair loss, Mirmirani says, because it permanently destroys the hair follicles. There are several reasons why you might be losing your hair. According to Agbai, genetics, hormonal shifts, stress, underlying medical conditions, nutritional deficiencies, and scalp inflammation are notable factors. Some research, including a 2024 review, suggests that there may be a connection between vitamin D deficiency and alopecia.
Steps to Treat Hair Loss Based on Cause
Ginseng contains certain phytochemicals that may promote hair growth on your scalp. But further research is needed to recommend specific dosages. If you are taking a new medication and notice your hair is falling out or thinning, reach out to your healthcare provider. Someone poisoned with arsenic, thallium, mercury, boric acid, and lithium can lose hair as a side effect. Ingesting large amounts of warfarin, an ingredient in rat poison, can also lead to hair loss.
She may also have early hereditary loss, which isn’t so obvious. Once your dermatologist has this information, it’s often possible to tell you what’s causing your hair loss. A 2020 study tracked 79 women taking spironolactone daily (doses ranged from 25–200 mg) for a minimum of 6 months. Nearly two-thirds of participants experienced some kind of improvement after 1 year.
Vitamin D
When you see a doctor to see what's causing your hair loss, they’ll probably start with a physical exam and ask about your diet, family history, and medical history. They may ask whether any of your relatives have hair loss. You can lose hair during menopause as your estrogen and progesterone levels drop. Also, because hair follicles shrink during this time, your hair might be thinner, fall out easier, and grow more slowly. The Food and Drug Administration has approved a low-level laser device as a treatment for hereditary hair loss in men and women. A few small studies have shown that it improves hair density.
Does COVID-19 cause hair loss? - News-Medical.Net
Does COVID-19 cause hair loss?.
Posted: Tue, 12 Jul 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Some signs of traction alopecia include hair loss in patches where the hair was pulled and shorter strands of hair near the forehead. Taking hormones can change hair growth all over your body. Masculinizing hormone therapy (taking testosterone) may cause hair loss within a year, and the effects aren't reversible if you stop hormone treatment. Because hair is constantly falling out and growing, hair loss often goes unnoticed. You're more likely to notice it when a lot of hair enters the resting phase at the same time or if hair roots become damaged during the growth process. During a hair transplant procedure, a dermatologist or cosmetic surgeon removes hair from a part of the head that has hair and transplants it to a bald spot.
A typical hair transplant involves removing patches of hair from your head and reinserting the hair follicle by follicle into the bald sections. With minoxidil, you might also see hair growing in places other than your scalp (cheeks and forehead, for example). Wash your face after you apply minoxidil and make sure you avoid other areas when you apply it.
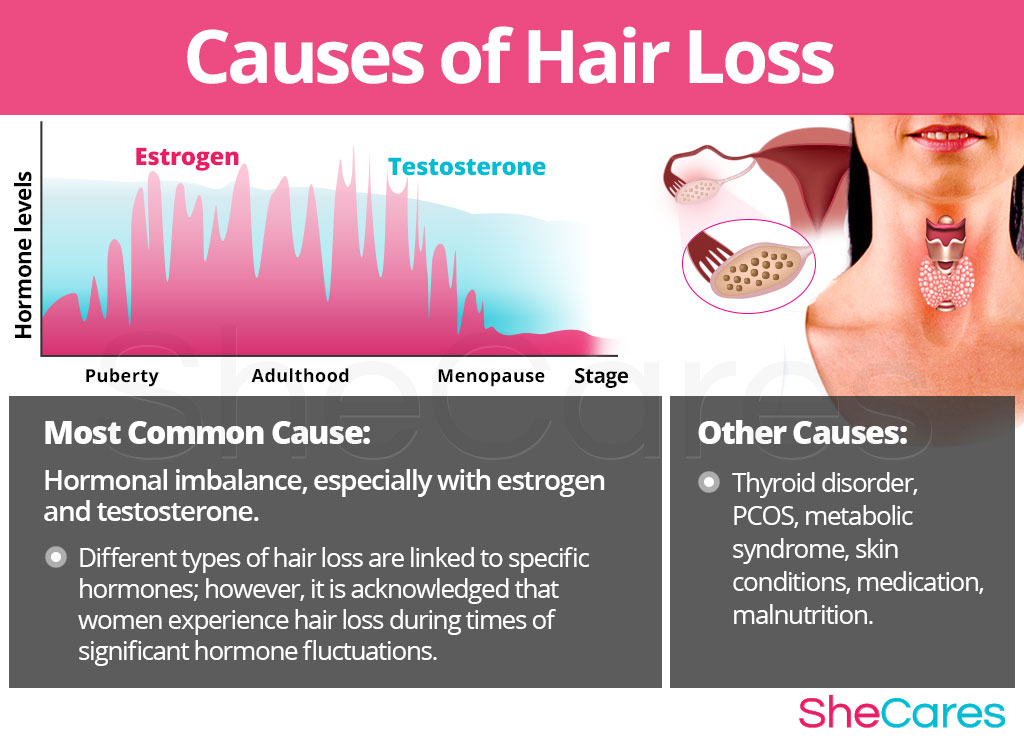
In men, hair loss is often caused by reactions to the predominant male reproductive hormone, testosterone. Many factors affect these levels, with other diseases or conditions leading to different types of hair loss. Natural hormonal shifts as you age can bring on hair loss. In women, androgenic alopecia can start to set on during the reproductive years, occurring later than it does in men.
Hair loss and hair thinning can be temporary or permanent. It’s usually genetic, but it can also be triggered by diseases or disorders that attack the hair follicles. Iron, folic acid, and zinc help hair grow thick and strong. Having a deficiency in these vitamins may affect your hair growth.
If you have alopecia, you can help hold onto your tresses by avoiding behaviors that are known to contribute to temporary and permanent hair loss, Mirmirani says. Spironolactone (Aldactone) is sometimes prescribed for people who have thinning hair related to aldosterone production (hyperaldosteronism). While technically a diuretic or “water pill,” that may be prescribed for high blood pressure or edema, Aldactone is an anti-androgen, too. Best known by its brand name Rogaine, minoxidil is an over-the-counter hair loss treatment approved by the FDA.
But illness, hormonal changes, stress, aging and inherited conditions can interfere with your hair’s growth cycle. More hair falls out, but new strands don’t always grow back. Excessive hair fallout from taking medication is usually temporary. Hair may stop shedding when you stop taking the medication.
Styling techniques, such as tight braids, can cause hair loss from the root, a condition called traction alopecia. Often these practices can cause permanent damage to the follicles over time. It helps to have a dermatologist who understands differences in hair type and can advise in healthy styling practices. A common cause of this imbalance is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It leads to cysts on a woman’s ovaries, along with other signs and symptoms, which can include hair loss.
No comments:
Post a Comment